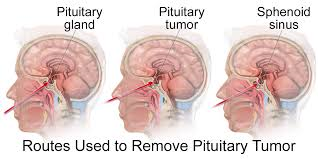
Hormonal balance is essential for the proper functioning of the body. The pituitary gland, often dubbed the “master gland,” plays a pivotal role in regulating various hormones that control crucial bodily processes. However, disorders of the pituitary gland can lead to significant hormonal imbalances, which may result in serious medical conditions. One medication commonly used to address these issues is Cabergoline, an ergot derivative that is highly effective in treating conditions like pituitary tumors and related hormonal imbalances.
This article explores the mechanism, uses, benefits, and potential side effects of Cabergoline, with a focus on the 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg doses. Understanding how Cabergoline works can shed light on its role in managing conditions like prolactinomas and hyperprolactinemia, among other hormone-related disorders.
What is Cabergoline?
Cabergoline is a dopamine receptor agonist that primarily works by inhibiting the release of prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Elevated levels of prolactin, known as hyperprolactinemia, can cause various problems in both men and women, such as infertility, irregular menstrual cycles, decreased libido, and in severe cases, the development of prolactin-secreting tumors called prolactinomas.
Cabergoline is often prescribed in two common doses: Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg. The lower dose is usually given initially, with the dosage being gradually increased depending on how the patient responds to the treatment.
Mechanism of Action
Cabergoline works by stimulating dopamine D2 receptors in the pituitary gland. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that naturally inhibits the production of prolactin. When Cabergoline binds to these receptors, it mimics the action of dopamine, reducing the amount of prolactin secreted by the pituitary gland. This is particularly beneficial in conditions where prolactin levels are abnormally high, leading to various health issues.
Uses of Cabergoline
- Treating Prolactinomas
Prolactinomas are benign tumors of the pituitary gland that secrete excessive prolactin. High prolactin levels can interfere with reproductive functions, leading to symptoms such as irregular or absent menstrual periods in women, milk production in women who are not pregnant or breastfeeding, and reduced testosterone levels in men. Cabergoline helps shrink these tumors and normalize prolactin levels, often leading to the restoration of fertility and other hormone-related functions.
- Managing Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. While prolactin is crucial for milk production after childbirth, elevated levels outside of pregnancy or lactation can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance. In both men and women, hyperprolactinemia can cause sexual dysfunction, bone loss due to reduced estrogen or testosterone levels, and infertility. Cabergoline effectively lowers prolactin levels, alleviating these symptoms and restoring hormonal balance.
- Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (Off-label use)
Although Cabergoline is primarily used for treating prolactin-related conditions, it has also been used off-label for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. As a dopamine agonist, Cabergoline can help increase dopamine levels in the brain and alleviate some of the motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s, such as tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement).
- Suppressing Lactation
In women who have given birth but do not wish to breastfeed, or in certain medical conditions where breastfeeding is not advised, Cabergoline can be used to suppress lactation. By reducing prolactin levels, the medication helps to prevent or stop milk production.
- Assisting with Growth Hormone Imbalances
Although not as common, Cabergoline can sometimes be used to treat acromegaly, a condition caused by excessive growth hormone production. In some cases, Cabergoline helps reduce the secretion of growth hormone, especially in patients who also have elevated prolactin levels.
Benefits of Cabergoline
- Effective Tumor Shrinkage
One of the significant benefits of Cabergoline is its effectiveness in shrinking prolactinomas. Studies have shown that the drug not only reduces prolactin levels but also leads to a reduction in tumor size in many patients, which can help alleviate symptoms like headaches and vision problems caused by the pressure of the tumor on surrounding structures.
- Improved Fertility
By normalizing prolactin levels, Cabergoline often restores fertility in women suffering from hyperprolactinemia. The regularization of menstrual cycles and ovulation can make it easier for women to conceive. In men, reducing prolactin levels can improve testosterone levels, which positively impacts sperm production and sexual health.
- Non-Surgical Treatment Option
For individuals with prolactinomas, Cabergoline offers a non-invasive alternative to surgery. In many cases, patients can avoid the risks and recovery time associated with surgery, making Cabergoline a preferred first-line treatment for prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors.
- Rapid Action
Cabergoline has a relatively long half-life, which allows for less frequent dosing compared to other prolactin-lowering medications. Patients often experience a noticeable improvement in their symptoms within just a few weeks of starting treatment.
Dosage: Cabergoline 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg
Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg are the two common doses used for treating pituitary-related conditions. The medication is usually taken once or twice a week, rather than daily, which increases patient compliance.
- Starting Dose: In most cases, treatment begins with the lower dose of Cabergoline 0.25 mg taken twice a week. This allows the body to adjust to the medication while minimizing potential side effects.
- Adjustment: Depending on the patient’s response, the dose can be increased to Cabergoline 0.5 mg per week or more, as needed. Some patients may require even higher doses, but this must be closely monitored by a healthcare provider.
Side Effects and Risks
While Cabergoline is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, particularly at higher doses or when treatment is initiated too rapidly. Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Constipation
These symptoms often subside as the body adjusts to the medication. However, some patients may experience more severe side effects, such as:
- Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure): Cabergoline can cause a drop in blood pressure, especially when standing up, leading to dizziness or fainting.
- Heart Valve Issues: Long-term use of Cabergoline, particularly in high doses, has been associated with an increased risk of developing fibrosis, or thickening of heart valves. Regular monitoring through echocardiograms may be recommended for patients on long-term treatment.
- Mental Health Symptoms: Rarely, Cabergoline may cause changes in mood or behavior, including depression or compulsive behaviors like gambling. Any changes in mental state should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
Precautions and Contraindications
Cabergoline is not suitable for everyone. It should not be used in patients with a history of heart valve disorders, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or certain lung conditions. Additionally, women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should consult their doctor before taking Cabergoline, as its effects on pregnancy are not fully understood. Breastfeeding is contraindicated while on this medication due to its prolactin-lowering effects.
Conclusion
Cabergoline is a powerful and effective treatment for hormonal imbalances caused by pituitary tumors and hyperprolactinemia. Its ability to reduce prolactin levels, shrink tumors, and restore fertility makes it a cornerstone therapy for many individuals facing pituitary-related issues. While generally well-tolerated, it is important for patients to be aware of potential side effects and to work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.