Introduction: In the digital era, the exchange of personal details has become a pivotal aspect of numerous industries, including the realm of financial protection. This section delves into the intricate relationship between the individuals who facilitate the transfer of sensitive information and the companies that provide financial safeguards. It explores how the collection and analysis of these details can directly influence the costs associated with obtaining such safeguards.
As we navigate through the vast digital landscape, our every click and purchase leaves a trail of data that is meticulously gathered and analyzed. This information is not merely a byproduct of our online activities but a valuable commodity that can significantly affect our financial dealings. The entities that manage this data play a crucial role in shaping the policies and premiums we encounter in the market for financial protection.
Understanding the Dynamics: The interplay between those who handle vast amounts of personal data and the institutions that offer financial safeguards is complex. It involves a delicate balance between the need for transparency and the desire for privacy. This article aims to shed light on how the information we inadvertently share can be used to determine the prices we pay for various forms of financial coverage.
By examining the mechanisms through which personal details are collected, analyzed, and utilized, we can gain a deeper insight into the factors that influence the pricing structures of financial protection services. This understanding is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the digital world with a sense of security and control over their personal information.
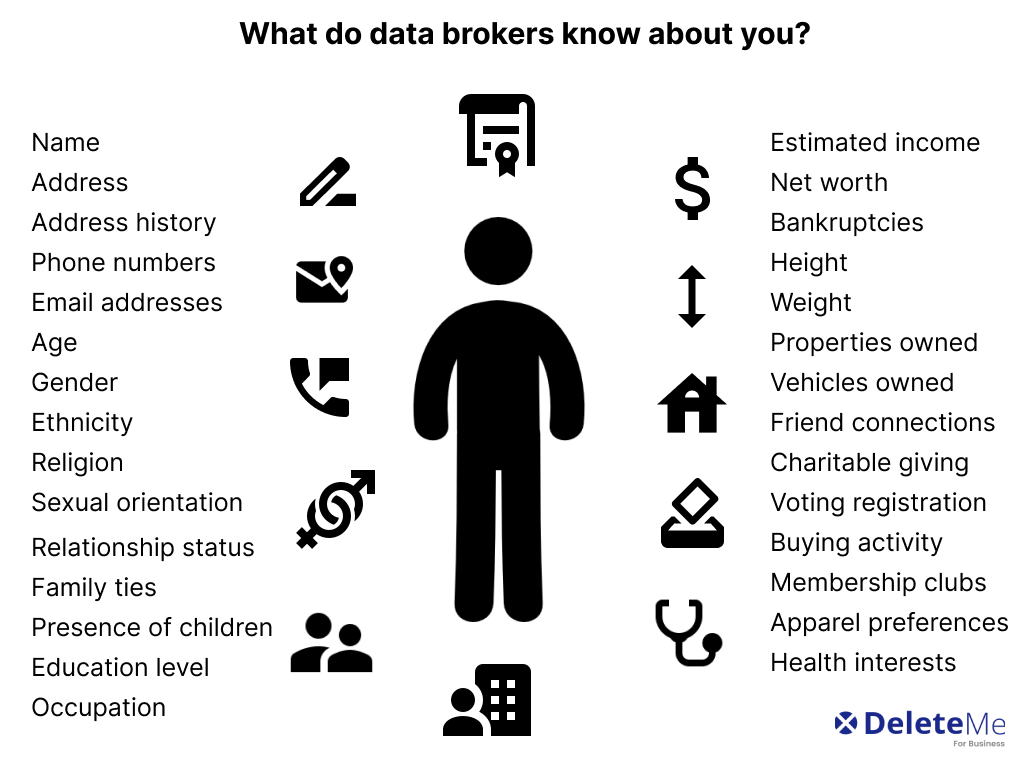
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the pivotal role of information aggregators in contemporary society. These entities serve as intermediaries, collecting and distributing vast amounts of personal details across various platforms. Their influence extends into numerous sectors, impacting both economic and social dynamics.
Information aggregators operate by gathering personal data from multiple sources, including public records, social media, and online transactions. They compile this information into comprehensive profiles, which are then sold to interested parties. This process plays a crucial role in the digital economy, facilitating targeted advertising, risk assessment, and market analysis.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Aggregators gather personal details from various sources, creating detailed profiles. |
| Data Distribution | These profiles are sold to businesses, marketers, and other entities seeking specific consumer insights. |
| Market Influence | Their activities impact market dynamics by enabling targeted marketing and personalized pricing strategies. |
The role of these aggregators is multifaceted, influencing not only commercial activities but also privacy norms and regulatory frameworks. As society becomes increasingly data-driven, understanding their operations and implications becomes essential for maintaining a balanced digital ecosystem.
Role of Data Aggregators in Modern Society
In the contemporary digital landscape, entities known as data aggregators play a pivotal role. These organizations collect, compile, and distribute vast amounts of information, influencing various aspects of modern life. This section delves into the mechanisms by which these aggregators gather and trade information, shedding light on their operational practices and societal impacts.
Data Collection Techniques
Data aggregators employ a variety of methods to amass information. These include web scraping, where software automatically extracts data from websites, and data mining, a process that involves sifting through large datasets to discover patterns and relationships. Additionally, many aggregators purchase data from other sources, such as retailers and social media platforms, further expanding their databases.
The Sale of Information
Once collected, this information is often sold to third parties, including marketers, researchers, and various service providers. The sale typically involves anonymizing the data to protect individual identities, although concerns about re-identification persist. The transactions are governed by contracts that dictate how the data can be used, though enforcement of these agreements can be challenging.
Impact on Society
The activities of data aggregators have profound implications for society. On one hand, they enable more personalized and efficient services, from tailored advertising to enhanced healthcare. On the other hand, they raise significant privacy concerns, as detailed personal profiles can be assembled without individuals’ explicit consent or knowledge. This dichotomy underscores the need for robust regulatory frameworks to balance the benefits of data aggregation with the protection of personal privacy.
In conclusion, data aggregators are integral to the functioning of modern society, facilitating the flow of information that drives numerous industries. However, their role also necessitates careful consideration of ethical and legal standards to safeguard individual rights and maintain public trust in digital technologies.
Mechanisms of Data Collection and Sale
This section delves into the intricate processes by which information is gathered and traded, shedding light on the practices that underpin the modern digital economy. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for recognizing the implications they have on individual privacy and the broader societal impacts.
Data Harvesting Techniques
Organizations employ a variety of methods to collect data. These range from simple web tracking tools that monitor online activities to more sophisticated algorithms that analyze social media interactions and purchasing histories. Each technique aims to extract valuable insights that can be used to tailor services or predict behaviors.
The Role of Data Aggregators
Data aggregators play a pivotal role in this ecosystem. They compile vast amounts of information from disparate sources, creating comprehensive profiles that are then sold to interested parties. This process often occurs without explicit consent from the individuals whose data is being aggregated, raising significant concerns about transparency and consent.
The Sale and Distribution of Data
Once collected, this information is often packaged and sold through various marketplaces. Buyers can include advertisers, financial institutions, and other entities seeking to enhance their decision-making processes. The sale of data is typically governed by contracts that dictate how the information can be used, though enforcement of these agreements can be challenging.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
The collection and sale of data raise numerous ethical and legal questions. Privacy advocates argue that individuals should have more control over their personal information, including the right to know how it is being used and the ability to opt out of data collection. Legal frameworks are evolving to address these concerns, but they often struggle to keep pace with technological advancements.
In conclusion, the mechanisms of data collection and sale are complex and multifaceted, involving a range of technologies and stakeholders. As society becomes increasingly digital, understanding these processes is essential for safeguarding privacy and ensuring that personal information is used responsibly.
Impact of Data Brokers on Consumer Privacy
This section delves into the profound influence that information intermediaries have on the confidentiality of personal details. As these entities gather and distribute vast amounts of data, their activities significantly shape the landscape of personal privacy. Understanding their operations is crucial for comprehending the broader implications on individual security.
Information intermediaries operate by collecting a plethora of personal details from various sources. These can include browsing histories, purchase records, and even social media activities. The aggregated data is then often sold to third parties, including those in the financial sector, who use it to inform their decision-making processes.
- **Data Collection Methods**: Intermediaries employ sophisticated techniques to amass data, ranging from cookies and tracking pixels to more invasive methods like data scraping.
- **Data Usage**: The information procured is frequently utilized to create detailed profiles of individuals, which can be used to predict behavior and tailor services or products.
- **Privacy Concerns**: This extensive data collection raises significant concerns about the erosion of privacy. Individuals often have little control over how their information is used once it has been collected by these entities.
The impact of these practices on consumer privacy is multifaceted. On one hand, the availability of detailed personal information can lead to more personalized services. However, this comes at the cost of reduced privacy and increased vulnerability to data breaches and misuse of information.
- **Increased Transparency**: Consumers are increasingly demanding more transparency in how their data is collected and used.
- **Regulatory Responses**: Various jurisdictions have enacted laws to protect consumer privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
- **Consumer Education**: There is a growing need for education on how to protect personal information and manage privacy settings effectively.
In conclusion, the role of information intermediaries in the realm of consumer privacy is a critical issue that requires ongoing attention. Balancing the benefits of data-driven services with the protection of personal privacy remains a significant challenge for both policymakers and consumers alike.
Insurance Industry and Data Utilization
In this section, we delve into the intricate ways in which the insurance sector harnesses vast amounts of information to refine its operations and enhance decision-making processes. The integration of sophisticated data analytics has transformed traditional underwriting and risk assessment methodologies, leading to a more tailored approach in the industry.
Insurers today are equipped with advanced tools that allow them to analyze a plethora of personal and behavioral data. This analysis is pivotal in determining the risk profiles of individuals, which in turn influences the pricing of policies. The following table illustrates the types of data commonly utilized by insurers and their respective applications:
| Type of Data | Application in Insurance |
|---|---|
| Demographic Information | Used to assess general risk factors associated with age, gender, and location. |
| Health Records | Informs health and life insurance premiums based on medical history and current health status. |
| Credit Scores | Helps in evaluating the financial stability of an individual, impacting policy pricing. |
| Driving History | Crucial for determining auto insurance rates, reflecting on past driving behaviors and incidents. |
| Online Activity | Analyzes digital footprints to gauge lifestyle habits and potential risks. |
The utilization of such data not only aids in more accurate risk assessment but also enables insurers to offer personalized products and services. However, this practice raises significant concerns regarding privacy and the ethical use of personal information. As the industry continues to evolve, it is imperative for regulatory bodies and insurers to strike a balance between innovation and consumer protection.
How Insurers Leverage Consumer Data
In the realm of risk assessment and financial planning, entities that provide coverage have increasingly turned to comprehensive analysis of individual profiles to refine their strategies. This section delves into the mechanisms by which these entities utilize detailed information about individuals to enhance their underwriting processes and tailor their offerings.
Insurers today are equipped with sophisticated tools that enable them to scrutinize vast arrays of personal details. These details range from basic demographic information to more intricate behavioral patterns. By analyzing this data, insurers can predict potential risks more accurately and adjust their premiums accordingly. For instance, a comprehensive review of an individual’s health records, lifestyle choices, and even social media activity can provide insights into their overall health and longevity, which are critical factors in determining health insurance premiums.
Moreover, the integration of advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms has allowed insurers to segment their customer base more effectively. This segmentation is not merely based on traditional factors such as age, gender, and location, but also on more nuanced variables like spending habits, credit scores, and response to previous marketing campaigns. Such detailed segmentation allows insurers to offer personalized products and services that better meet the specific needs of each segment, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and retention.
Additionally, the use of predictive modeling in insurance is revolutionizing the way claims are processed. By leveraging historical data and predictive analytics, insurers can anticipate the likelihood of future claims and proactively manage risks. This not only helps in setting appropriate premiums but also in designing preventive measures that can reduce the incidence of claims, benefiting both the insurer and the insured.
In conclusion, the strategic use of consumer data by insurers is transforming the industry, enabling more precise risk assessment and personalized service offerings. As technology continues to evolve, the sophistication with which insurers analyze and apply this data will likely increase, further shaping the landscape of risk management and financial protection.
Data-Driven Underwriting Practices
In this section, we delve into the methodologies employed by underwriters to assess risk and set premiums. The focus is on how personal details are utilized to make these critical decisions, shaping the financial landscape for policyholders.
Risk Assessment: At the core of underwriting lies the evaluation of potential hazards associated with insuring an individual. This process involves a meticulous analysis of various factors that could influence the likelihood of a claim. These factors range from demographic details such as age and occupation to behavioral patterns derived from digital footprints.
Premium Determination: The insights gathered through this analysis directly impact the pricing of policies. For instance, individuals who exhibit behaviors that are statistically correlated with higher risks might face increased premiums. Conversely, those with a profile indicating lower risk might benefit from more favorable rates.
Data Utilization: The advent of sophisticated data analytics has revolutionized this field. Underwriters now have access to vast arrays of information, enabling them to make more nuanced assessments. This data-driven approach not only enhances the precision of risk predictions but also allows for a more tailored approach to each policyholder.
However, the reliance on such extensive data collection raises significant ethical and privacy concerns. It is imperative for the industry to balance the benefits of data-driven underwriting with the need to protect individual privacy and ensure fair practices.
In conclusion, the integration of advanced data analytics into underwriting practices represents a significant shift in the insurance industry. It offers the potential for more accurate risk assessment and personalized pricing but also necessitates careful consideration of the ethical implications and privacy safeguards.
The Influence of Personal Data on Premiums

In this section, we delve into the intricate relationship between individual information and the financial costs associated with certain services. The focus here is on understanding how to opt out of Whitepages listings the collection and analysis of personal details can directly impact the pricing structures of essential services, particularly in the financial sector.
Personal Information Collection: In today’s digital age, numerous entities gather a vast array of personal details. This information ranges from basic demographic data to more sensitive financial and behavioral patterns. The rationale behind this extensive collection is often linked to enhancing service provision and tailoring offerings to individual needs.
Impact on Pricing: The utilization of this collected data has a profound effect on the pricing of services such as loans, credit facilities, and particularly, premiums in the realm of financial protection services. Companies use sophisticated algorithms to analyze this data, which in turn influences the risk assessment and pricing models they employ.
Data Analysis and Premium Determination: The analysis of personal data allows companies to categorize individuals into different risk groups. Those perceived as higher risk may face increased costs for the same services offered to lower-risk individuals. This practice, while beneficial for risk management, raises significant concerns regarding fairness and transparency in pricing.
Consumer Awareness and Action: It is crucial for consumers to be aware of how their data is being used to determine service costs. Understanding this linkage empowers consumers to take proactive steps in managing their data and advocating for more transparent practices. This awareness can lead to better data protection measures and more equitable pricing structures.
In conclusion, the influence of personal data on the pricing of financial services, particularly premiums, is a complex and evolving issue. It underscores the need for robust data protection laws and increased consumer education on data privacy and its financial implications.
Online Privacy Concerns

In today’s interconnected world, the safeguarding of personal information has become a paramount concern. As technology advances, so do the methods by which sensitive details are collected and utilized. This section delves into the current challenges facing digital privacy, highlighting the evolving threats and the implications for individuals and organizations alike.
Current Threats to Digital Privacy
The landscape of digital privacy is continually shifting, with new risks emerging as frequently as new technologies are developed. One of the most pressing concerns is the unauthorized access to personal data by malicious actors. Cybercriminals employ sophisticated techniques to infiltrate systems, steal information, and exploit it for financial gain or other nefarious purposes.
Another significant threat is the overcollection of data by legitimate entities. Companies often gather more information than necessary, sometimes without clear consent or transparency about how it will be used. This practice can lead to data breaches and misuse, as seen in numerous high-profile cases where sensitive customer details were exposed.
Moreover, the use of tracking technologies, such as cookies and other monitoring tools, raises concerns about continuous surveillance and the erosion of individual privacy. These tools can track user behavior across the web, building detailed profiles that can be used for targeted advertising or other purposes that may infringe on personal freedoms.
Legislation and Privacy Protections
In response to these threats, various legislative measures have been enacted to protect digital privacy. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States aim to give individuals more control over their personal information. These regulations require companies to be transparent about data collection practices and to implement robust security measures to protect user data.
However, the effectiveness of these laws is continually tested as technology evolves and new loopholes are discovered. Thus, ongoing vigilance and adaptation of legal frameworks are necessary to keep pace with the dynamic nature of digital privacy threats.
In conclusion, the challenges to digital privacy are multifaceted and require concerted efforts from individuals, corporations, and governments to address effectively. Awareness, robust legislation, and technological safeguards are all crucial components in the fight to protect personal information in the digital age.
Current Threats to Digital Privacy
In today’s interconnected world, the safeguarding of personal information has become a paramount concern. This section delves into the various challenges that threaten the confidentiality of individual data, exploring how these issues impact our daily lives and the measures being taken to address them.
The landscape of digital privacy is fraught with numerous risks that can compromise the security of sensitive information. Below is a table summarizing some of the most prevalent threats:
| Threat Type | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cyber Attacks | Unauthorized access to systems or networks to steal or manipulate data. | Can lead to significant data breaches, affecting millions of users. |
| Phishing | Deceptive practices aimed at tricking individuals into revealing personal information. | Results in identity theft and financial fraud. |
| Data Mining | The extraction of information by companies for commercial use without explicit consent. | Invasion of privacy and potential misuse of personal details. |
| Spyware | Software that secretly monitors and collects user data without their knowledge. | Breaches privacy and can lead to unauthorized data access. |
These threats underscore the importance of robust legislative frameworks and technological safeguards. As we navigate through an era where personal data is increasingly valuable, understanding these risks is crucial for effective protection.
Legislation and Privacy Protections
In the evolving landscape of digital interactions, the role of regulatory frameworks is pivotal in safeguarding individual rights. This section delves into the mechanisms by which laws and policies aim to protect personal information, ensuring that users maintain control over their digital footprints.
Current Legal Frameworks
Various jurisdictions have enacted legislation to address the growing concerns around data misuse. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe establishes stringent rules for data handlers, emphasizing transparency and consent. Similarly, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) empowers residents with the right to know about and control the use of their personal information by businesses.
Enhancing Privacy Protections
These laws not only impose obligations on entities that collect and process data but also provide individuals with specific rights. Users can request access to their data, demand its deletion, or opt out of its sale. Such provisions are crucial in a world where personal information is a valuable commodity.
Challenges in Enforcement
Despite the existence of robust laws, enforcement remains a challenge. The complexity of global data flows often complicates the application of national regulations. Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancements can outstrip the ability of lawmakers to keep legislation current.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, there is a clear need for continuous updates to legal frameworks to address emerging threats and technologies. This includes enhancing cross-border cooperation to ensure that data protections are not undermined by jurisdictional discrepancies. Additionally, public awareness campaigns are essential to educate consumers about their rights and the tools available to protect their privacy.
In conclusion, while legislation plays a critical role in protecting privacy, it must evolve in tandem with the digital environment. Continuous engagement from policymakers, businesses, and consumers is necessary to maintain a balance between innovation and individual rights.
Consumer Awareness and Data Control

In this section, we delve into the critical role that individual understanding and proactive measures play in safeguarding personal information. As the digital landscape evolves, it becomes increasingly important for consumers to be vigilant and informed about the management of their sensitive details.
Awareness begins with recognizing the various channels through which personal information is collected and utilized. Consumers must educate themselves about the practices of data aggregation and the potential risks associated with these activities. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about the sharing and protection of their personal data.
To effectively control personal information, consumers should employ a variety of strategies. Regular monitoring of privacy settings on digital platforms is essential. Adjusting these settings to the most secure options can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data access. Additionally, using strong, unique passwords for different accounts and enabling two-factor authentication can enhance security.
Another effective strategy is to limit the amount of personal information shared online. This includes being cautious about the details included in social media profiles and the types of applications granted access to personal data. Consumers should also be wary of phishing attempts and suspicious emails that may seek to extract sensitive information.
Furthermore, staying updated on the latest privacy laws and regulations can help consumers understand their rights and the protections afforded to them. Engaging with advocacy groups and participating in community discussions about data privacy can also contribute to a broader awareness and collective action against data misuse.
In conclusion, enhancing consumer awareness and taking proactive steps to control personal information are vital in today’s digital age. By understanding the mechanisms of data collection and the implications of data misuse, individuals can better protect themselves against potential threats and maintain control over their personal data.
Mitigating Data Risks in Insurance
In the realm of modern financial services, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. This section delves into the strategies and practices employed by the industry to minimize potential vulnerabilities associated with the handling of personal details. It explores how companies are adapting to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data they manage.
Current Threats to Digital Privacy
The digital landscape is fraught with challenges that threaten the privacy of individuals. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it crucial for insurers to stay ahead of these threats. Common risks include unauthorized access to databases, phishing attacks, and malware designed to extract confidential client details.
One significant concern is the rise in sophisticated hacking techniques that target financial institutions. These attacks not only jeopardize the security of customer records but also undermine trust in the industry. Additionally, the misuse of personal information for fraudulent activities is a growing issue that requires immediate attention.
Another prevalent threat is the exploitation of data through social engineering tactics. These methods involve manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. As these threats continue to evolve, it becomes imperative for insurers to implement robust security measures.
To combat these challenges, insurers are adopting advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance their security protocols. These tools help in identifying patterns and anomalies that could indicate a breach, thereby enabling proactive measures to be taken.
Moreover, regular audits and compliance checks are essential in maintaining the integrity of data systems. These practices ensure that all security protocols are up-to-date and effective against the latest threats. Education and training for employees are also critical components in the fight against digital threats, as awareness can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches.
In conclusion, while the digital privacy landscape remains complex and ever-changing, the insurance industry is taking significant steps to mitigate risks. By embracing advanced technologies, implementing stringent security measures, and fostering a culture of awareness, insurers are better equipped to protect the sensitive information of their clients.
Strategies for Protecting Personal Information
In the digital age, safeguarding one’s sensitive details from potential breaches is paramount. This section delves into practical methods individuals can employ to fortify their personal security, ensuring that their confidential data remains protected from unauthorized access and exploitation.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Before implementing protective measures, it is crucial to comprehend the current landscape of digital threats. Cybercriminals employ sophisticated techniques to access personal details, ranging from phishing scams to malware attacks. Awareness of these tactics is the first step in developing a robust defense strategy.
Implementing Strong Passwords
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect personal information is by using strong, unique passwords for each online account. Passwords should include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters, making them difficult to crack. Additionally, changing passwords regularly can further enhance security.
Utilizing Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring not only a password and username but also something that only the user has on them, like a piece of information only they should know or possess. This could be a fingerprint, a face recognition, a PIN, or a security token. Implementing 2FA can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Regularly Updating Software
Keeping all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date is essential. Updates often include security patches that protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities. Neglecting to update software can leave personal information exposed to potential threats.
Being Cautious with Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them a prime target for hackers. Avoid accessing sensitive accounts or entering personal details while connected to public Wi-Fi. If necessary, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt the connection and protect the data being transmitted.
Educating Yourself on Scams
Stay informed about the latest scams and fraudulent activities. Being aware of common tactics used by cybercriminals can help you recognize and avoid potential threats. Regularly check for updates on new scams and educate family members, especially those who may be less tech-savvy.
In conclusion, protecting personal information in today’s digital world requires proactive measures and continuous vigilance. By understanding the threats, implementing strong security practices, and staying informed, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of their sensitive data falling into the wrong hands.



