Coagulation issues, which influence the blood’s capability to clump, can have serious well-being consequences. The perception of the position that CSL plasma proteins play in those disorders is integral for both clinical professionals and patients. In this article, we’ll discover the precise plasma proteins involved in coagulation, their features, and how abnormalities in these proteins can lead to diverse coagulation problems.
By way of the give-up, you may have a complete perception of the types of plasma proteins, the 4 major plasma proteins, and how those abundant plasma proteins contribute to maintaining ordinary clotting strategies. And here’s a little bonus: if you’re planning a plasma donation soon, then usage of a CSL Plasma Coupon Code ought to make the experience even extra rewarding.
The Critical Role of CSL Plasma Proteins in Blood Clotting Issues
Plasma proteins are fundamental for the blood’s coagulation system, assisting in regulating and preserving normal clotting. When those proteins feature nicely, they prevent excessive bleeding by forming clots at injury sites. Nonetheless, irregularities or a lack of plasma proteins can prompt coagulation issues, consisting of haemophilia, profound vein apoplexy, or spread intravascular coagulation (DIC), in which the blood either clumps an unreasonable amount or excessively little.
This is the role of CSL plasma proteins, and you know what the role of the coupon code is. The role of a coupon code is to provide you with maximum benefit. If you are a plasma donor and want to get more benefits from a donation of plasma, use the $1000 promo code at CSL. It gives you the maximum incentive for the donation of plasma. This is a win-win situation for you.
Understanding CSL Plasma Proteins
Plasma proteins are still up in the air in the blood plasma, that is the fluid part of the blood that remains after dark red and white platelets are dispensed with. Plasma itself is composed of water, electrolytes, hormones, and the dissimilation of proteins; every serving has unique functions within the frame.
Types of plasma proteins
The types of plasma proteins include egg whites, globulins, fibrinogen, and thickening components, among others. These proteins assume vital roles in various physiological strategies, which incorporate protecting osmotic equilibrium, safe reactions, and blood coagulation.
- Albumin: Most plasma proteins are capable of controlling blood volume by keeping up with the osmotic strain.
- Globulins: These are partitioned into alpha, beta, and gamma globulins, with gamma globulins being pivotal for invulnerable highlights.
- Fibrinogen: A vital participant in coagulation, fibrinogen is changed into fibrin all through the thickening framework, shaping the underlying premise of blood coagulation.
- Clotting elements: These are exact proteins worried about the coagulation overflow, a complicated series of exercises that lead to the development of a strong blood clump.
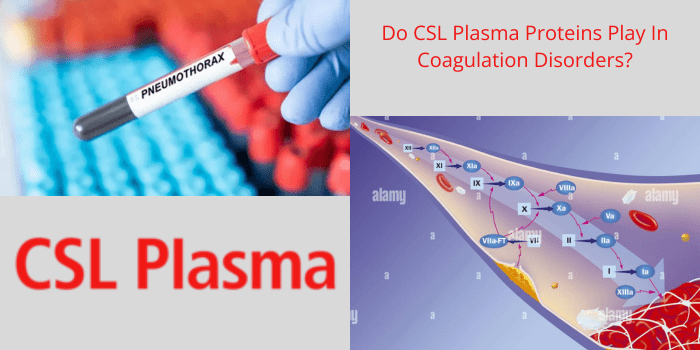
How CSL Plasma Proteins Contribute to Coagulation
The 4 major plasma proteins—albumin, globulins, fibrinogen, and clotting elements—work collectively to make certain that blood clots shape effectively and at the proper time. Here’s a closer study of how plasma proteins are involved in coagulation:
- Initiation of Clotting: At the point when a vein is harmed, thickening variables are enacted in a particular succession, known as the coagulation overflow. This outpouring eventually results in the change of fibrinogen to fibrin, shaping a cross-section that traps platelets and structures coagulation.
- Law of Clot Formation: Plasma proteins ensure that clotting takes place solely while vital. Proteins like antithrombin and protein C modify the clotting procedure with the aid of inhibiting clot formation when it isn’t always needed, preventing conditions like thrombosis.
- Stabilisation of Clots: Fibrin, fashioned from fibrinogen, is the primary structural factor of a clot. Plasma proteins play a role in stabilising those clots, making sure they stay intact until the damage is healed.
Coagulation Disorders Linked to CSL Plasma Proteins
Abnormalities in CSL plasma proteins can lead to numerous coagulation disorders. Underneath are a few examples:
- Haemophilia: A hereditary problem wherein specific coagulating components (along with factor VIII or IX) are inadequate, prompting radical draining even from minor mishaps.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This situation happens when blood coagulation structures in a profound vein, consistently in the legs. It very well may be dangerous if the coagulation is removed and goes to the lungs, causing a pneumonic embolism.
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC): an outrageous illness wherein extreme coagulation happens at some stage in the casing, draining thickening elements and prompting serious death.
What Is the Role of Abundant Plasma Proteins in Coagulation?
The abundant plasma proteins, especially fibrinogen and egg whites, are major in the coagulation cycle. Fibrinogen’s transformation to fibrin is integral to clump arrangement, while egg whites work to protect blood degree and strain in a roundabout way, helping the circulatory device’s ability to answer hurt.
- Fibrinogen: As an abundant plasma protein, fibrinogen’s function in forming fibrin is vital for effective clotting. Deficiencies or abnormalities in fibrinogen can cause bad clot formation and excessive bleeding.
- Albumin: even though not immediately concerned with clotting, albumin’s role in retaining blood volume is crucial for general circulatory fitness, which supports effective coagulation.
Plasma proteins function beyond coagulation.
Plasma proteins, while quintessential for coagulation, also carry out an inequality of other critical features within the body. They play a key role in the immune response, with globulins—specifically gamma globulins—performing as antibodies that guard the body from infections.
Moreover, proteins like albumin are concerned with nutrient shipping, carrying hormones, vitamins, and minerals all through the frame. Plasma proteins also contribute to retaining the body’s pH balance, serving as buffers that neutralise excess acids or bases to ensure balance in the body’s internal environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CSL plasma proteins play an imperative role in the frame’s coagulation methods, ensuring that blood clots form when desired and stopping excessive bleeding. The types of plasma proteins concerned with coagulation, along with the 4 major plasma proteins, are essential for retaining the everyday clotting features. Abnormalities in those proteins can result in serious coagulation issues; however, advances in plasma-derived treatment options and ongoing research provide a wish for higher remedy selections.
Understanding the functions of plasma proteins and their role in coagulation is essential for coping with and treating coagulation disorders. By making sure that those abundant plasma proteins function correctly, we can maintain the delicate stability of clotting that is integral to fitness and well-being.
If you know about Stroke Stem Cells like Stroke Stem Cells Treatment at Biotherapy International.